


: Enge Split-pole Spectrometer
: Description of the HKS
: HKS Aerogel Cerenkov counter
To separate protons and K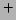 s, another type of Cerenkov counters
will be installed behind the second TOF walls.
Figure 26 shows the refraction index dependence of the
number of photo electrons for proton and K
s, another type of Cerenkov counters
will be installed behind the second TOF walls.
Figure 26 shows the refraction index dependence of the
number of photo electrons for proton and K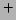 from the Cerenkov counter.
In our momentum region of interest (around 1.2 GeV/
from the Cerenkov counter.
In our momentum region of interest (around 1.2 GeV/ ), a proton emits
over 50% Cerenkov photons of those for K
), a proton emits
over 50% Cerenkov photons of those for K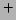 in lucite (n=1.48); hence,
the on-line separation of proton was not easy with the lucite Cerenkov counters
for the E89-009 experiment. Figure 27 shows estimated ADC spectra
for water and lucite Cerenkov counters with a Monte Carlo simulation.
Cerenkov light emission of proton in water is much smaller because of
the smaller reflective index of 1.33 and, thus, water Cerenkov is better
for the K
in lucite (n=1.48); hence,
the on-line separation of proton was not easy with the lucite Cerenkov counters
for the E89-009 experiment. Figure 27 shows estimated ADC spectra
for water and lucite Cerenkov counters with a Monte Carlo simulation.
Cerenkov light emission of proton in water is much smaller because of
the smaller reflective index of 1.33 and, thus, water Cerenkov is better
for the K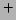 , p separation in this momentum region.
Two layers of counters (HWC1 and HWC2) are necessary to achieve
on-line rejection efficiency of
, p separation in this momentum region.
Two layers of counters (HWC1 and HWC2) are necessary to achieve
on-line rejection efficiency of
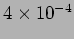 for protons,
which corresponds to the proton contamination rate in the kaon trigger below 100 Hz.
Wavelength shifters such as amino-G-salt and 4-methyl-umbelliferone could be doped in water
to make light response isotropic and to increase number of Cerenkov photons
unless they deteriorate proton rejection efficiency.
Simulation study and test with a prototype are in progress.
for protons,
which corresponds to the proton contamination rate in the kaon trigger below 100 Hz.
Wavelength shifters such as amino-G-salt and 4-methyl-umbelliferone could be doped in water
to make light response isotropic and to increase number of Cerenkov photons
unless they deteriorate proton rejection efficiency.
Simulation study and test with a prototype are in progress.
A test experiment for the prototypes of the
aerogel, water and lucite Cerenkov counters is scheduled at KEK-PS with 1 2 GeV/
2 GeV/ p and
p and  in winter, 2001 (KEK PS-T494).
With the result of this test beam time, the design of Cerenkov counters
and option of the radiator (water or lucite, with and without wavelength shifter) will be finalized.
in winter, 2001 (KEK PS-T494).
With the result of this test beam time, the design of Cerenkov counters
and option of the radiator (water or lucite, with and without wavelength shifter) will be finalized.



: Enge Split-pole Spectrometer
: Description of the HKS
: HKS Aerogel Cerenkov counter
Satoshi N. Nakamura
�$BJ?@.�(B16�$BG/�(B12�$B7n�(B2�$BF|�(B
![]() 2 GeV/
2 GeV/![]() p and
p and ![]() in winter, 2001 (KEK PS-T494).
With the result of this test beam time, the design of Cerenkov counters
and option of the radiator (water or lucite, with and without wavelength shifter) will be finalized.
in winter, 2001 (KEK PS-T494).
With the result of this test beam time, the design of Cerenkov counters
and option of the radiator (water or lucite, with and without wavelength shifter) will be finalized.