



: HKS acceptance
: High resolution Kaon Spectrometer
: Basic design of the
�$BL\
Optics and detector geometries
A 3D magnetic field calculation with OPERA3D-TOSCA was performed for each magnet,
to include all higher term effects into the simulation.
With this magnetic field map calculated by TOSCA (figure 23) and
the optimized parameters by TRANSPORT, the GEANT Monte-Carlo simulation was carried out
to estimate the HKS momentum resolution and the acceptance.
Table 6 summarizes the optimized magnetic field parameters and the
geometrical conditions for the HKS magnets.
The parameters used in the simulation are summarized in table 7.
�$BI=�(B 6:
Summary of the HKS TRANSPORT calculation
| Item |
Given or Optimized values |
| |
|
| Q1 length (cm) |
84 |
| Q1 bore radius (cm) |
12 |
| Q1 field gradient (T/m) |
-5.78 |
Q1 integral field gradient (T/m m) m) |
-5.54 |
| Q2 length (cm) |
60 |
| Q2 bore radius (cm) |
14.5 |
| Q2 field gradient (T/m) |
3.40 |
Q2 integral field gradient (T/m m) m) |
2.53 |
|
Dipole bending angle (degrees) |
70 |
| Radius of D magnet center (cm) |
270 |
| D gap (cm) |
20 |
| Dipole Field (T) |
1.44 |
In the simulation, the realistic shape of apertures of Q1 and Q2 (figures 18
and 19), walls of the target chamber, and walls of the
dipole vacuum chamber are all taken into account.
Red lines shown in figure 4 show kaon trajectories in the horizontal plane
(emission angles in horizontal plane, 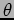 = 4.3, 7, 9.7
= 4.3, 7, 9.7 ) with momenta of
1.05, 1.20, 1.35 GeV/
) with momenta of
1.05, 1.20, 1.35 GeV/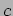 , obtained with the GEANT simulation code.
The horizontal focusing property of the HKS is clearly seen.
, obtained with the GEANT simulation code.
The horizontal focusing property of the HKS is clearly seen.
�$BI=�(B 7:
Summary of parameters used in the HKS simulation
| Description |
Value |
Virtual target position(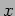 points e-arm points e-arm |
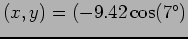 cm cm
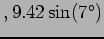 cm) cm) |
side, 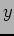 -axis is along Hall C beam line) -axis is along Hall C beam line) |
|
| Target |
Carbon 100 mg/cm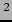 |
| Splitter rotation angle |
8.51 with respect to beam line with respect to beam line |
| Splitter field |
1.49 T |
Splitter bending angle (1.2 GeV/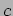 ) ) |
14.5 |
| Collimator position |
20 cm upstream from Q1 entrance |
| Distance from virtual target to Q1 |
105 cm |
| HKS rotation angle |
21.5 with respect to beam line with respect to beam line |
| Central momentum |
1.2 GeV/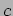 |
| Central scattering angle |
7 |
| Optics |
R34=0 (vertically point to point focus) |
| Beam energy |
1.8 GeV |
| Beam size |
50 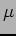 m m 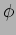 |
| Kaon momentum |
1.0 to 1.4 GeV/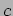 |
| |
(1.2 GeV/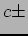 12.5% for detector size study) 12.5% for detector size study) |
| Kaon angular distribution |
0 to 15 to 15 uniform uniform |
Active areas of the HKS detectors are determined
requiring the momentum acceptance of 1.2 GeV/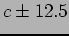 %
and maximizing the geometrical acceptance.
Figure 8 shows beam profiles at each detector.
The active area of each detector is indicated by a square in the figure and
listed in table 15.
%
and maximizing the geometrical acceptance.
Figure 8 shows beam profiles at each detector.
The active area of each detector is indicated by a square in the figure and
listed in table 15.




: HKS acceptance
: High resolution Kaon Spectrometer
: Basic design of the
�$BL\
Satoshi N. Nakamura
�$BJ?@.�(B16�$BG/�(B12�$B7n�(B1�$BF|�(B